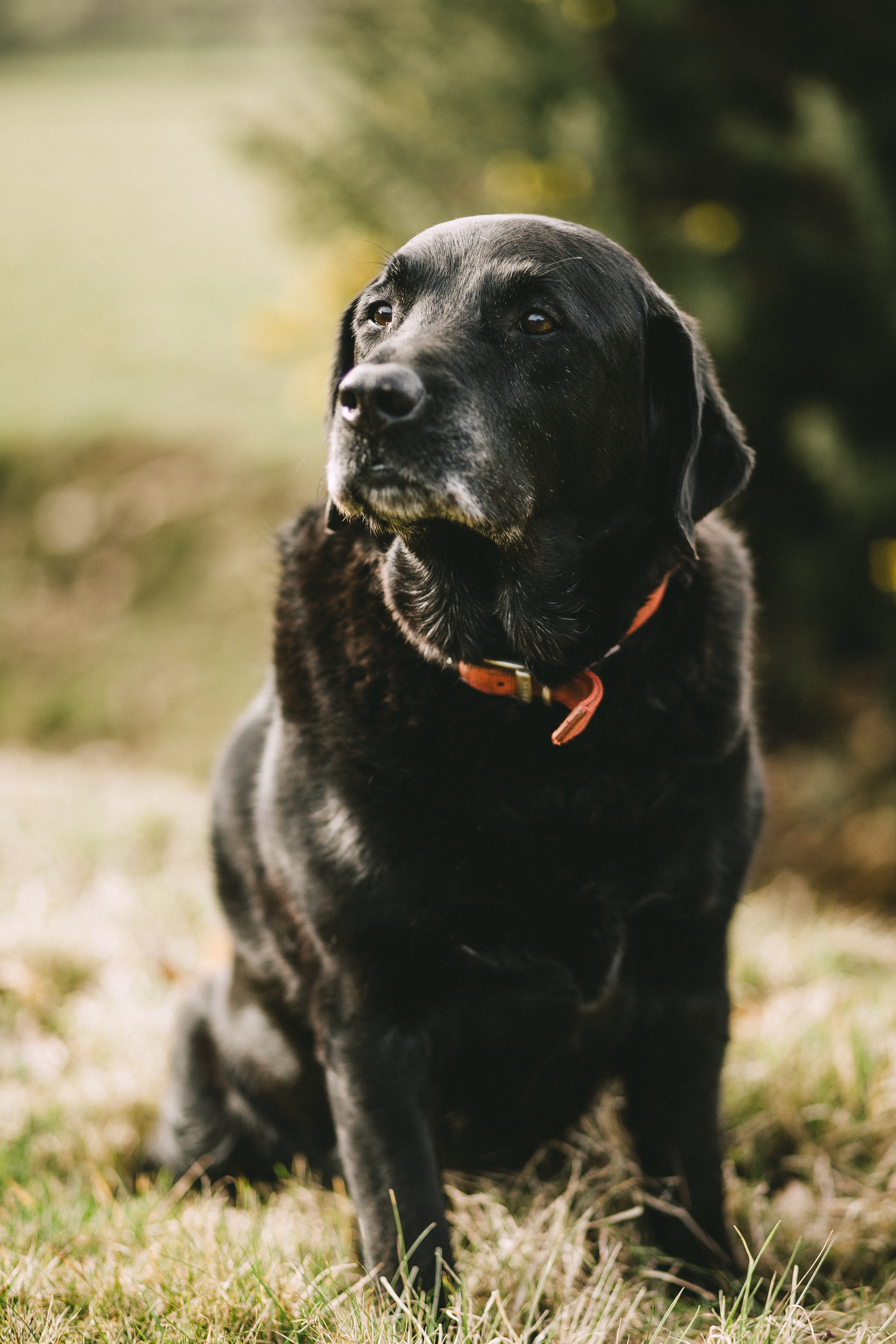
This study wanted to evaluate the importance of some supplemental vitamins and trace elements and diet in the protection against rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using a prospective cohort study of old women. They found that the highest amounts of ingested supplemental vitamin C and vitamin E had a positive impact on RA, whereas no association could be found with carotenoids, lycopene or lutein/zeaxanthin. Supplemental zinc was also inversely associated with RA. Supplemental copper and manganese only showed a positive trend on RA, in the same way as greater amounts of fruit and cruciferous vegetables. However, only beta-cryptoxanthin and supplemental zinc showed a statistically significant risk reduction on RA, while diets rich in fruit and cruciferous vegetables only revealed a possible protective effects.
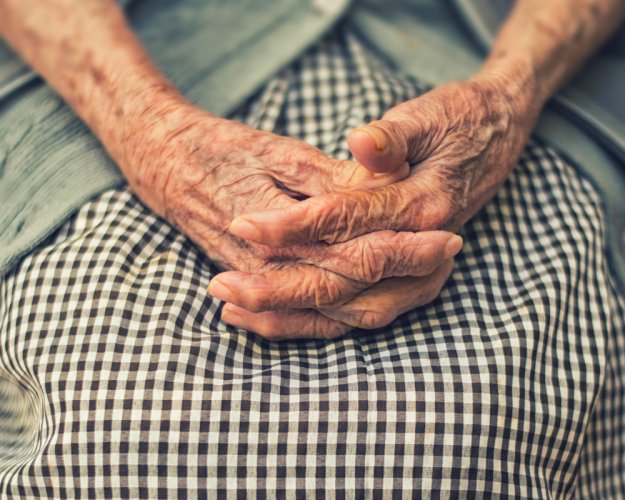

Antioxidant micronutrients and risk of rheumatoid arthritis in a cohort of older women.
Cerhan, J.R. et al.
 Purina: Your Pet, Our Passion
Purina: Your Pet, Our Passion